AWS::S3::Bucket
- Store
objects(files) inbuckets(directories) - Buckets have a globally unique name
- All operations are
strong consistent: after write/delete in an object (PUT/DELETE), a subsequent read (GET) will have the latest version of the object - By default, S3 objects are
ownedby theAWS accountthatuploadedit
Objects
key: the unique identification for the object is itsfull path. E.g., s3://my-bucket/my-folder/my-file.txtsize: Max objectsizeis 5TB (but upload must happen with 5GB chunks)metadata: list of key-value pairstags: up to 10version: version id
MFA Delete
- Multiple confirmations required for deleting
- To permanently delete a version, to suspend the versioning, etc
- Only root account can enable/disable this option through the CLI
# enable MFA delete (must be root account)
aws s3api put-bucket-versioning \
--bucket "my-bucket" \
--versioning-configuration "Status=Enabled,MFADelete=Enabled"
Requester Pays
- Charger the
3rd partywho is willing to request data to your bucket for thenetwork costsonly - The owner will pays for the
storage costs - requester must be authenticated in AWS

Pre-signed URL
Pre-Signed URL: URLs valid for a limited time (3600s by default)- For downloads, CLI can be used
-
For uploads, SDK can be used
-
Access multiple operations GET, PUT, POST, ...
# generate pre-signed URL for an object
aws s3 presign "s3://mybucket/myobject.txt" --region "sa-east-1"
aws s3 presign "s3://mybucket/myobject.txt" --region "sa-east-1" --expires-in "300" # 3600 by default
```
## Performance
- `3500` PUT/COPY/POST/DELETE per second per prefix
- `5000` GET/HEAD per second per prefix
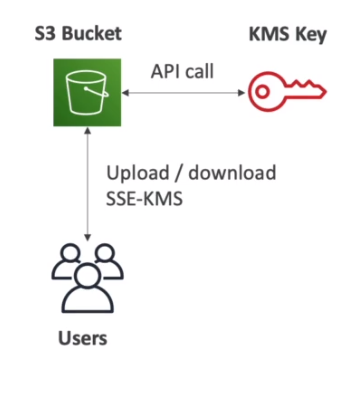
- `KMS` limits the performance because KMS has a per-request quota
- `Multi-part upload`
- It is recommended for files > 100MB and required for files > 5GB
- It parallelize the upload and achieve higher throughput
- `S3 Byte-Range Fetches`
- Optimizes READ
- Parallelize GET requests
- Can also be used to retrieve only a part of the file (e.g., only the header)
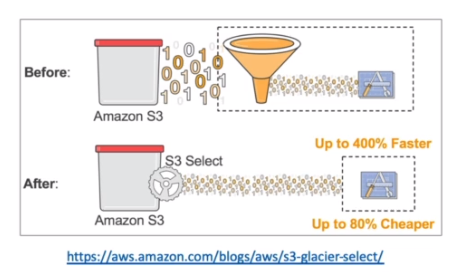
- `S3 Select & Glacier Select`
- Allow queries to the S3 using `SQL language` (server-side filtering)
- Avoid unnecessary data filtering by the application
- Can also search in a csv file
- Less network traffic!
## Properties
- <https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/aws-resource-s3-bucket.html>
```yaml
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Properties:
AccelerateConfiguration:
AccelerateConfiguration
AccessControl: String
AnalyticsConfigurations:
- AnalyticsConfiguration
BucketEncryption:
BucketEncryption
BucketName: String
CorsConfiguration:
CorsConfiguration
IntelligentTieringConfigurations:
- IntelligentTieringConfiguration
InventoryConfigurations:
- InventoryConfiguration
LifecycleConfiguration:
LifecycleConfiguration
LoggingConfiguration:
LoggingConfiguration
MetricsConfigurations:
- MetricsConfiguration
NotificationConfiguration:
NotificationConfiguration
ObjectLockConfiguration:
ObjectLockConfiguration
ObjectLockEnabled: Boolean
OwnershipControls:
OwnershipControls
PublicAccessBlockConfiguration:
PublicAccessBlockConfiguration
ReplicationConfiguration:
ReplicationConfiguration
Tags:
- Tag
VersioningConfiguration:
VersioningConfiguration
WebsiteConfiguration:
WebsiteConfiguration
AccelerateConfiguration
S3 Transfer Acceleration(S3TA)- Increase transfer speed
- Transfer to
AWS edge locationand forwards to target region
- With S3TA, you pay only for transfers that are accelerated
BucketEncryption
- SSE-S3
- Keys managed by AWS
- SSE: server side encryption
- Header "x-amz-server-side-encryption":"AES256"
- SSE-KMS
- Encryption and keys managed by KMS (key management service)
- User control, audit trail support, rotation policy of the key
- Header "x-amz-server-side-encryption":"aws:kms"
- SSE-C
- You manage your own keys
- Through CLI or SDK only (not console)
- HTTPS is mandatory because you have to pass the key to aws
- Key must be provided in the header in every request
- AWS just use the key to encrypt and discard it
- Header "x-amz-server-side-encryption":"aws:c"
- Client Side Encryption
- You encrypt the data and send it
-
S3 encryption SDK can help with that
-
A
default encryption methodcan be set for all files. Also, different methods can override the default encryption for each single file and version
CorsConfiguration
- CORS (
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing): get resource from another origin Web Browser Policy: allow requests to other origins only if this origin being requested allows CORS-
Origin: scheme (protocol) + host (domain) + port. E.g., https://www.example.com:443 -
Same origin: http://example.com/app1 & http://example.com/app2
-
Different origins: http://example.com/ & http://other.example.com/
-
Preflight Request
-
The browser will perform a
preflight requestto the target origin in order to check if it allows CORS. - It's a
OPTIONSrequest withHost(target origin) andOrigin(source origin) -
The target origin responds with the allowed methods
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.source-origin.comAccess-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, PUT, DELETE
-
S3 CORS
-
CORS must be enabled for the bucket in order to allow requests from other origins
- CORS is enabled and defined under
permissionsconfig in the bucket
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": ["Authorization"],
"AllowedMethods": ["GET"],
"AllowedOrigins": ["http://source-bucket.com"],
"ExposeHeaders": [],
"MaxAgeSeconds": 3000
}
]
- This responds with the following headers:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://source-bucket.com/Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET

<html>
<head>
<title>My First Webpage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>I love coffee</h1>
<p>Hello world!</p>
</body>
<img src="coffee.jpg" width="500" />
<!-- CORS demo -->
<div id="tofetch" />
<script>
var tofetch = document.getElementById("tofetch");
// load from URL in the same origin
fetch("extra-page.html")
.then((response) => {
return response.text();
})
.then((html) => {
tofetch.innerHTML = html;
});
// load from URL in different origin (CORS in the target origin must be enabled)
fetch(
"http://target-bucket.s3-website-eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/extra-page.html"
)
.then((response) => {
return response.text();
})
.then((html) => {
tofetch.innerHTML = html;
});
</script>
</html>
LifecycleConfiguration
- StorageClass
- Standard - General Purpose
- Durability 99.999999999%
- Availability 99,99%
- Use cases: big data analytics, mobile&gaming apps, content distribution
- Standard - Infrequent Access (IA)
- Infrequent access, but rapid access when needed
- Availability 99,9%
- Use cases: backups
- Intelligent Tiering
- Small monthly fee for monitoring and auto-tiering
- Automatically move objects between tiers. E.g. GA -> IA
- Availability 99,9%
- One Zone - Infrequent Access (IA)
- Same as Standard IA but in a single AZ
- Availability 99,5%
- Use cases: secondary backup
- Glacier
- $0.004/GB + retrieval cost
- Each archive has up to 40 TB
- Archive are stored in vaults
- Retrieval options: expedited (1-5min), standard (3-5h), bulk (5-12h)
- Minimum storage duration of 90 days
- Glacier Deep Archive
- Even cheaper!
- Retrieval options: standard (12h), bulk (48h)
- Minimum storage duration of 180 days


-
The
storage classof an object can be set for each file (upon uploading or afterwards) -
Lifecycle Rules
-
Lifecycle rules can be created under Management Tab
S3 Analyticscan be setup to automatically transition objects. Only Standard to Standard-IA-
Transition actions: E.g., move to Standard IA 60 days after creation and to glacier 6 months afterTransition current versionsof objects between storage classesTransition previous versionsof objects between storage classesExpire current versionsof objectsPermanently delete previous versionsof objectsDelete expired delete markersor incomplete multipart uploads

LoggingConfiguration
Access Logscan be stored in another s3 bucket. Do not store it in the same bucket otherwise it will loop foreverAPI callscan be logged incloudtrail- Can be activated under
Server Logging Accessin properties tab
NotificationConfiguration
- S3 Event Notifications
S3:ObjectCreated,S3:ObjectRemoved, ...- Events notification is defined under properties tab
- Rules can be applied to monitor only certain objects
-
Example of event notification use: generate thumbnail as soon as a jpg file is created in the bucket
-
Events can be sent to
SNS,SQSorLambda Functionsin order for the event to be further processed - The target broker (SNS, SQS, etc) must have access policies to allow s3 to publish in it
ObjectLockConfiguration
- Places an
Object Lockconfiguration on the specified bucket. - The default retention can also be override when you
explicitlyapply aretention periodto an object version (Retain Until Date) -
Different versions of an object can have different retention modes and periods
-
The rule specified in the Object Lock configuration will be
applied by default to every new objectplaced in the specified bucket -
The DefaultRetention specifies:
-
Mode
GOVERNANCE: users can't modify or delete versionsCOMPLIANCE: versions can't be overwritten (even by root)
-
Period
Retention PeriodLegal Hold(no expiry date)
-
For
archivesyou can add Vault Lock and adoptWORM(write once read many) - This way your archive cannot be modified/deleted. Good for compliance & audit!
PublicAccessBlockConfiguration
- Configuration to block
public accessto objects - This is used to prevent
data leaks - This configuration can also be applied at the
account level(for all buckets)
ReplicationConfiguration
CRR: Cross Region Replication-
SRR: Same Region Replication -
Copy is asynchronous
- Versioning must be enabled in order to replicate
- S3 must have proper
IAM permissions - Use cases: compliance, lower latency
- After activating, only
new objectsare replicated -
Replication
cannot be chained! Replica from 1 to 2 won't replicate from 2 to 3 -
Replication rule
- It's configured under
replication rulesin Management Tab - Replication can be activated for all objects or specific objects with filter
- For
DELETEoperations, you can choose whether the delete markers will be replicated
VersioningConfiguration
- Once you version-enable a bucket, it can
never return to an unversioned state - Versioning can only be
suspendedonce it has been enabled.Suspendingthe versioning won't remove the versions already created - With versioning, you can easily
recoverfrom both unintended user actions and application failures - When overriding a file, a
new versionis created - Objects with
version id nullmeans they were created when versioning was not activated - Deleted objects receive a
delete marker. And the previous versions of it are preserved. To delete an object completely, all the versions must be deleted
WebsiteConfiguration
- S3 can host static websites and have them accessible on the www
- Under bucket properties,
static website hostingmust be activated block public accessmust be disabled- A
bucket policymust enable access to its files
{
"Id": "Policy1633026957759",
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt1633026955731",
"Action": ["s3:GetObject"],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::hvitoi/*",
"Principal": "*"
}
]
}
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Webpage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>I love coffee</h1>
<p>Hello world!</p>
</body>
<img src="coffee.jpg" width="500" />
</html>